When considering the purchase of an electric guitar, you should know that there are thousands of different guitars available from a variety of different manufacturers, but they are all one of three main types – solid body, hollow body and semi-hollow body.
When considering the purchase of an electric guitar, you should know that there are thousands of different guitars available from a variety of different manufacturers, but they are all one of three main types – solid body, hollow body and semi-hollow body.
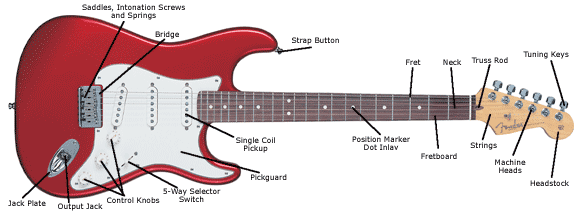
Types of Electric Guitars
Hollow body electric guitars were the first electric guitars. The pioneers in the 1930s simply added a pickup to existing acoustic models. The major drawback, which still exists today, is that the hollow body guitars resonate, which means when amplified they are prone to feedback.
The solid body guitar followed and by 1951 was a commercial success for Fender with Gibson soon to follow. Solid body guitars did not have the feedback problems of the hollow bodies and also produced much greater sustain.
In 1958 Gibson came out with the first semi-hollowbody guitar. It had a solid block of wood running through the middle of the body with resonant cavities above and below. It looked like a hollowbody guitar and had some of its resonance, but also shared the sustain of the solid body without the feedback associated with hollowbody instruments.
After the type and construction of the body, the neck of the guitar is key to both its sound and playability.
Guitar Necks
There are two main kinds of guitar necks – neck through body, which is found only in solid body guitars – and bolt-on or glued on necks. Fans of the neck through body set-up love it for the long sustain it produces. Glued-on necks are the traditional form of construction, while bolt-on necks were first used by Fender on their Telecaster-predecesors.
The type of wood used in the neck, due to its mass, affects the balance and tone of the instrument. Luthiers often use one wood for the neck – such as a lighter wood like basswood or mahogany – and a harder, denser wood – like rosewood, pau ferro or maple – for the fingerboard that will resist wear from playing.
Electric Guitar Pickups
Guitar construction and electronics work together to create the unique sound of each guitar. The most tweaked feature of the electronics is the pickups. The main choice is between the classic single coil pickup, which have a crisp, clear sound, but are prone to extraneous hum (though some modern single-coil pickups are engineered to avoid hum), and the fat sounding humbuckers, which use dual coils and magnets. Then there is pickup placement, with guitars having 2 or 3 pickups between the neck and bridge and switches to choose and mix between them for a wide range of sound.
Bridge Types
Finally, just past the pickups is the bridge. The basic bridge is the stoptail bridge, such as found on a Gibson Les Paul. There is also the vibrato bridge with the “whammy bar” that lets the guitar player easily bend all the strings at once, such as the classic Fender Stratocaster bridge.
The Bottom Line
Body, neck, pickups and bridge – those are the four key elements to the electric guitar. Add in the wide varieties of wood they are made from and the unique sound coloration each creates, and you have endless possibilities for making music.